Methods to Control Risks of Exposure
Work practice controls and engineering controls help prevent the transmission of bloodborne diseases in the workplace and allow you to perform job tasks with minimal risk of exposure.
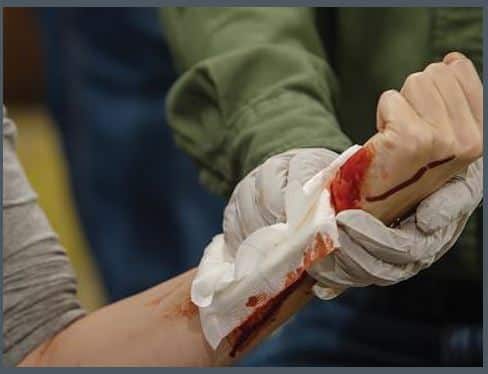
Work practice controls focus on the manner in which tasks are performed. For example, using personal protective equipment such as disposable gloves when performing first aid is considered a work practice control.
Engineering controls reduce workplace exposure by removing or isolating the hazard, such as providing an appropriate disposal container for needles. Your employer is required to examine and maintain or replace engineering controls on a regular basis.
Standard Precautions
Standard precautions are recommended for any scene where blood or other body fluids may be present. This means treating all body fluid as potentially infectious, even that of someone you know well.
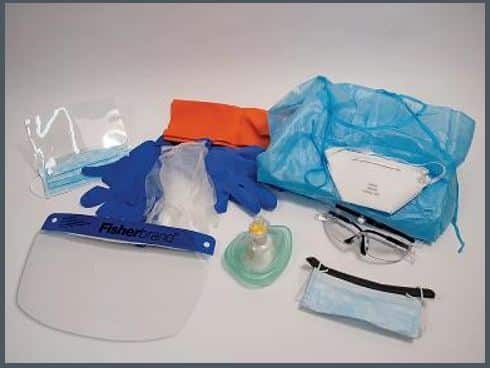
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is specialized clothing or equipment that isolates your body from contact with potentially infectious materials.
Examples of PPE include the following:
- Disposable gloves
- Protective eye/face shields
- Resuscitation masks or CPR barrier shields with one-way valves
Effective PPE must not permit potentially infectious materials to pass through or reach your skin, eyes, mouth, or clothes under normal conditions of use. Your employer will make PPE available to you in the appropriate size and at no cost. Non-latex alternatives will also be available to employees with allergic sensitivity to latex. Employers must also properly clean, launder, repair, replace, or dispose of contaminated PPE as needed.
Always wear disposable gloves when hand contact with blood or other body fluids is possible. Replace gloves as soon as possible when torn, punctured, contaminated, or if their ability to function as a barrier is compromised. Perform all actions involving blood or other potentially infectious materials in such a way as to minimize splattering, splashing, and spraying. If needed, wear face shields in situations where this could occur and pose a hazard to your eyes, nose, or mouth. Proper handling and disposal of needles/sharps, contaminated bandages, gauze, or linens are also important.
Knowledge Check
Standard precautions are the infection-control approach wherein all blood and body fluid is treated as potentially infectious.
